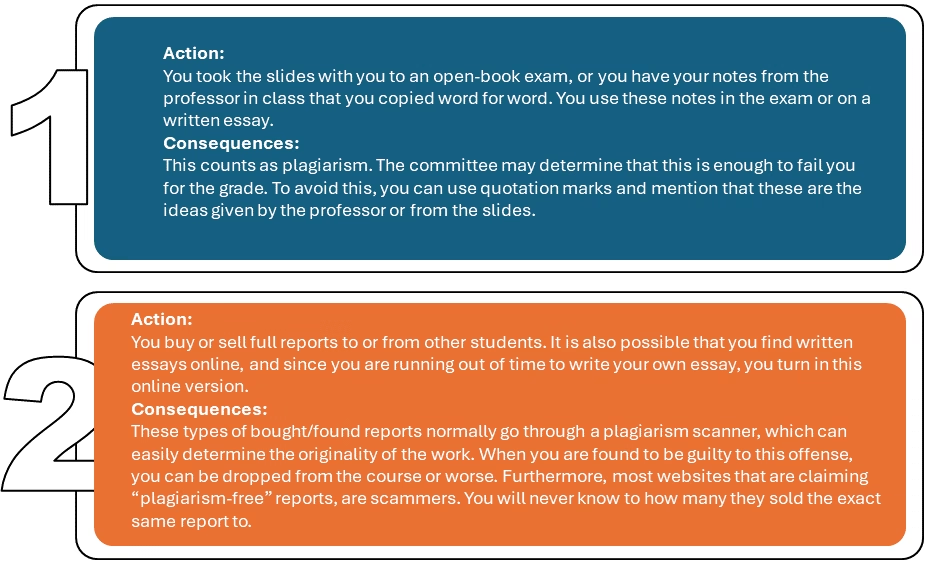
The consequences for committing plagiarism can be severe, including penalties such as receiving a failing grade or even expulsion from the university. Universities educate students on how to avoid plagiarism and the potential consequences of committing it. On my article on the different types of plagiarism, I ordered them in severity. Take a look there to see what is the most severe type of plagiarism.
1. Investigation & What happens afterwards?
Upon discovery of plagiarism, the incident will be reported to the dean for review. Typically, a meeting between the course supervisor, dean, and student will be held to determine the appropriate action. Minor incidents may be handled directly, while major incidents are typically overseen by a university committee. The student may also be required to seek external counseling. Each university has its own academic integrity committee, so the specific penalties may vary. Regardless, plagiarism should not be taken lightly as the consequences can be severe.