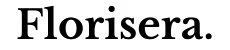A resistor is a fundamental two-terminal component used in countless electronic devices to limit or regulate electric current. Resistors are often marked with color bands to indicate their values. Typically, these resistors feature four or five color bands. Understanding how to read these color codes is essential for determining the resistor’s value. In this article, we’ll explore what resistor color codes are, how to read them, and provide a tool to help you find resistor values using color codes.
The figure below shows a resistor with four color bands on it: the first two bands represent digits, the third represents the multiplier, and the fourth represents the tolerance. The first two digits can be concatenated together and further multiplied. In the example below, this would involve concatenating 5 and 6 to get 56, then multiplying by 10, resulting in 560 Ohms. Notice the gap between the multiplier and tolerance band, this is an indication of which end is which.
A similar concept applies to a five-band resistor, where an extra digit allows for more precise resistance values. Scroll down to the chapter on 4-band or 5-band resistor color codes for the interactive tool (which only works on a desktop).

If you do not know which end is which, here are some tips that might help you:
- Try to fill it in from both ends, and look up in the table below (third section) to see if it fits any of the predetermined values in the E-series.
- Gold or silver is a very common tolerance color, look out for that color at the ends.
- There is normally a larger gap between the multiplier & tolerance bands than in between the other bands, look out for that.
- If there are only 3 bands visible, you can still obtain the value, but it means the tolerance might be 20% (only for very cheap resistors).
Resistor code: 4-band
To use the interactive resistor color code tool, click on the colors for the first, second, and third bands to set the digits and multiplier. Then, click the color for the fourth band to set the tolerance. The tool will display colored bands on the resistor and automatically calculate the resistance and tolerance.
Resistor code: 5-band
To use the interactive resistor color code tool, click on the colors for the first, second, and third bands to set the digits and multiplier. Then, click the color for the fourth band to set the tolerance. The tool will display colored bands on the resistor and automatically calculate the resistance and tolerance.
Summary of EIA Preferred or Standard Resistor Value Series
Resistor values are organized into sets of preferred or standard values, which follow a logarithmic sequence to ensure appropriate spacing relative to component tolerance. Tolerances typically range from ±20% to ±1%, with more accurate options available at higher cost. Standard values facilitate component selection across manufacturers, streamlining sourcing and reducing costs. In the table below I show the 4 most used series.
| E Series | Tolerance (Sig Figs) | Number of values in each decade |
|---|---|---|
| E3 | >20% | 3 |
| E6 | 20% | 6 |
| E12 | 10% | 12 |
| E24 | 5% [normally also available in 2% tolerance] | 24 |
The E12 series resistor values are also widely used within the industry. They provide a wider range of common resistor values that can be used in electronic circuit designs and this can be essential for many analogue designs.
| 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.5 |
| 1.8 | 2.2 | 2.7 |
| 3.3 | 3.9 | 4.7 |
| 5.6 | 6.8 | 8.2 |
Florius
Hi, welcome to my website. I am writing about my previous studies, work & research related topics and other interests. I hope you enjoy reading it and that you learned something new.
More Posts