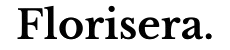The Physics and Technology of Extrinsic Semiconductors
Doping modifies a semiconductor by introducing donor or acceptor atoms, increasing free electron or hole concentration. This creates an n-type or p-type material, shifting the Fermi level closer to the conduction or valence band, respectively. The level of doping determines electrical conductivity and charge carrier behavior.
The Physics and Technology of Intrinsic Semiconductors
Semiconductors are materials with electrical properties between metals and insulators, governed by their band structure. The valence and conduction bands define electron movement, with a band gap influencing conductivity. Intrinsic semiconductors, free of impurities, require energy to excite electrons into the conduction band, enabling current flow. Carriers, including electrons and ...
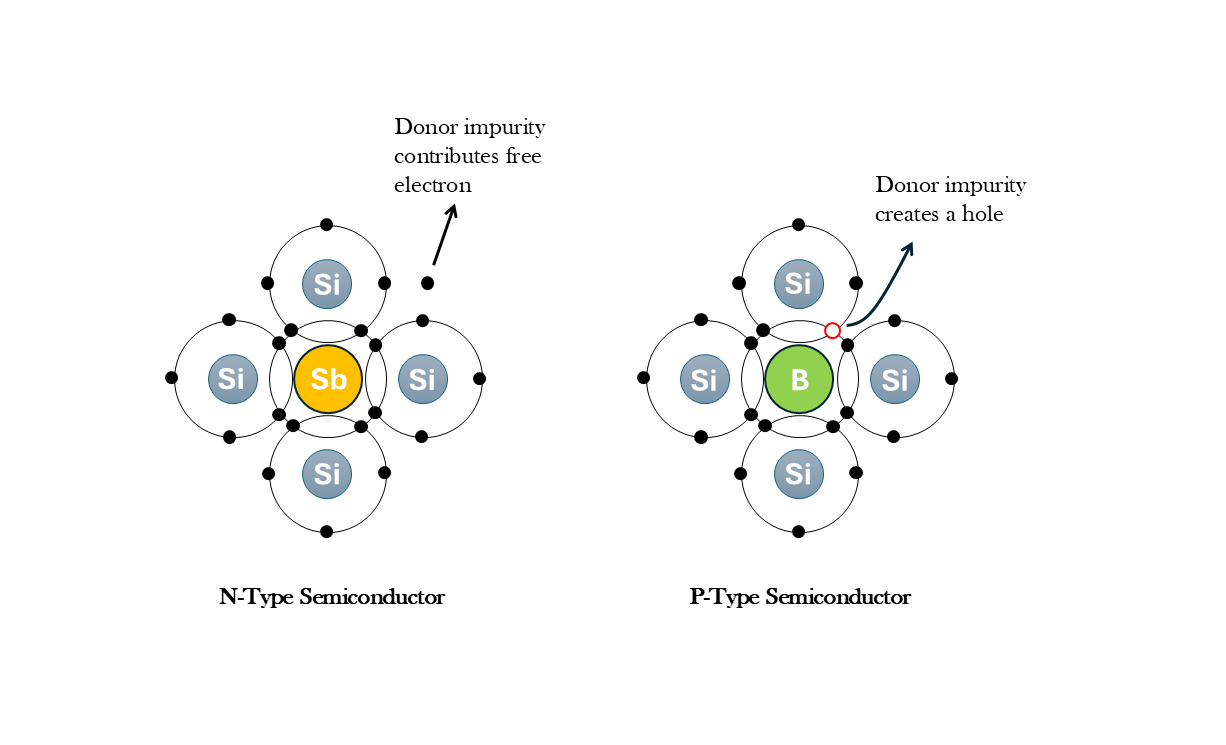
Majoranas: The Next Step in Quantum Computing
Microsoft’s Azure Quantum team is developing quantum chips using topological qubits, leveraging Majorana zero modes for stability. Their research on superconducting nanowires could accelerate quantum computing advancements. This article explains Majorana physics, its role in quantum systems, and Microsoft’s roadmap for scalable quantum computing, offering insights into this groundbreaking development.
Beyond Conductivity: Advanced Metal Science
Explore the advanced physics of metals beyond conductivity. Learn about superconductivity, AC conductivity, and electromagnetic interactions.
The Physics and Technology of Metals
Understanding the conductivity of metals involves exploring their high electron mobility, Ohm’s law, and quantum mechanical models like Drude and Sommerfeld. This article discusses how metals conduct electricity, the role of energy bands, and how electron interactions shape conductivity, highlighting key concepts like drift velocity, Fermi energy, and relaxation time.
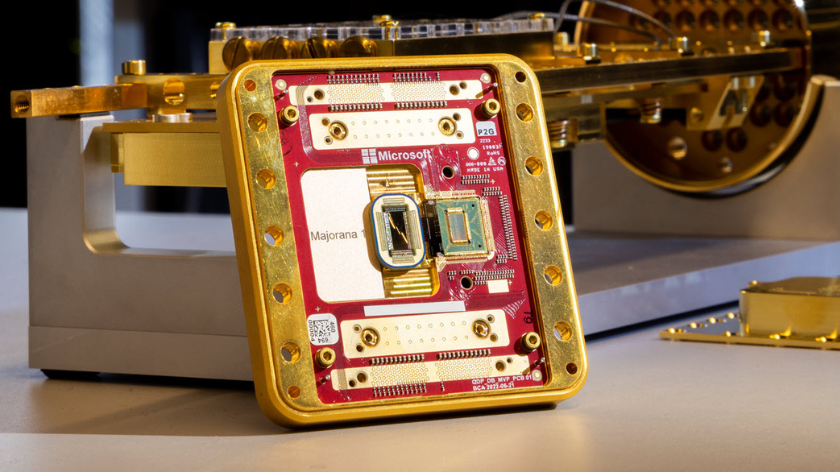
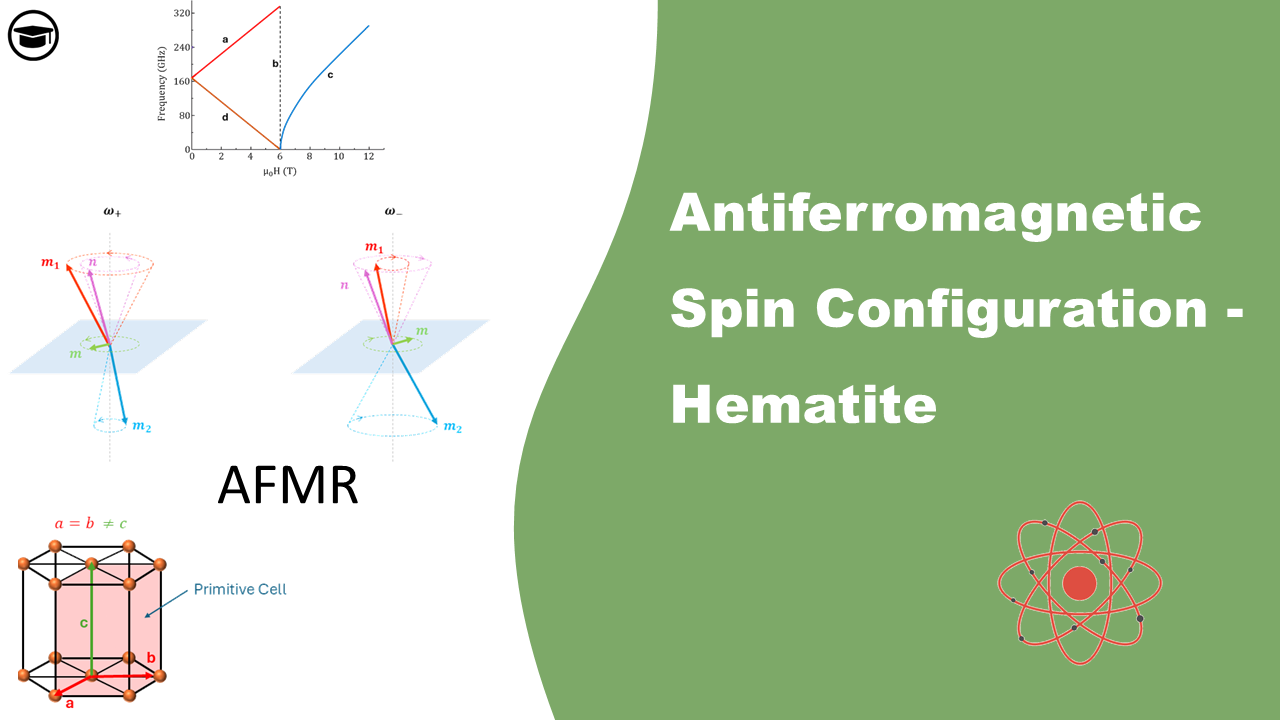
Antiferromagnetic Spin Configuration – Hematite
Explore the fascinating world of antiferromagnetic resonance, where materials like hematite and Yttrium Orthoferrite reveal the hidden dynamics of opposing magnetic moments. Dive into the science behind these unique materials, and discover how their properties open new possibilities in fields such as spintronics and data storage.
Electron Paramagnetic Resonance spectroscopy
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy, also called electron spin resonance (ESR), is a technique for studying materials with unpaired electrons, such as organic and inorganic radicals, and transition metal complexes. It functions by detecting magnetic properties of electrons. This post covers the science of EPR, its key components, real-world applications, ...
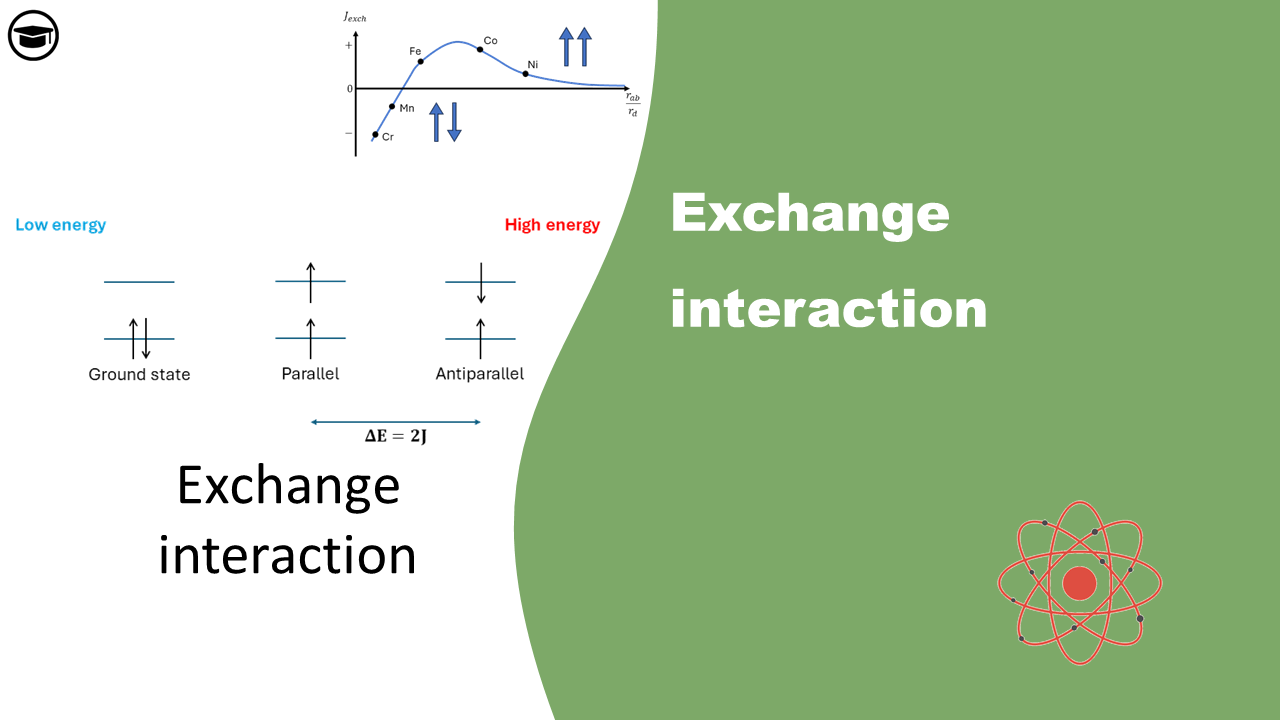
Exchange interaction
Electrons prefer parallel spins due to the quantum mechanical concept of exchange energy, which lowers their system's total energy. This preference is a result of the Pauli exclusion principle and the antisymmetric nature of fermion wavefunctions, reducing Coulomb repulsion and stabilizing the system in quantum mechanical interactions.
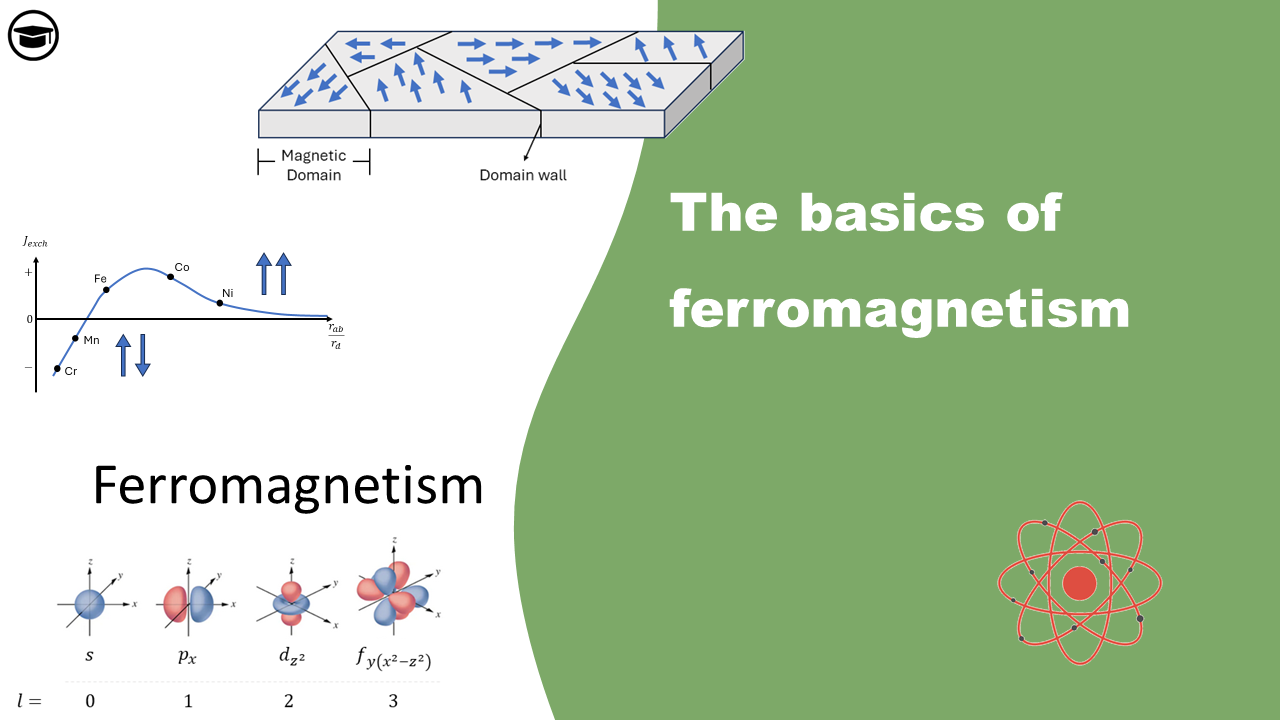
The basics of ferromagnetism
Magnetism is the force that is exerted by magnets when they repel or attract each other. It is caused by the motion of electric charges. Electrons can spin like tops, and they orbit
An introduction to Skyrmions
Skyrmions are a class of topological solitons discovered by Tony Skyrme in the 1960s, he used this concept to describe how subatomic particles exist as discrete entities in a nuclear field. The original idea was overshadowed by other theories, however, the same concept is now used to describe a phenomena ...