Minor vs Major Words?
Capitalization is an important aspect of writing, as it helps to make text clear, consistent, and easy to read. In general, there are two main ways to capitalize a sentence: title casing and sentence case. With title casing, every major word in the sentence is capitalized, while with sentence case, only the first word of the sentence is capitalized.
When deciding which words to capitalize, it’s important to keep in mind that not all words require capitalization. Generally, only nouns, pronouns, adjectives, and adverbs should be capitalized. Other words such as “the,” “an,” “of,” “by,” “for,” “in,” etc. should not be capitalized, unless they are the first word of the sentence.
It’s also important to note that the conventions for capitalization can vary depending on the type of writing you’re doing. For example, in academic and journalistic writing, there are different conventions for capitalizing words. For example, it’s generally recommended to capitalize the names of places, people, and organizations, while names of theories should only be capitalized when referring to the name of the founder of the theory (e.g. Riemann’s removable singularity theorem).
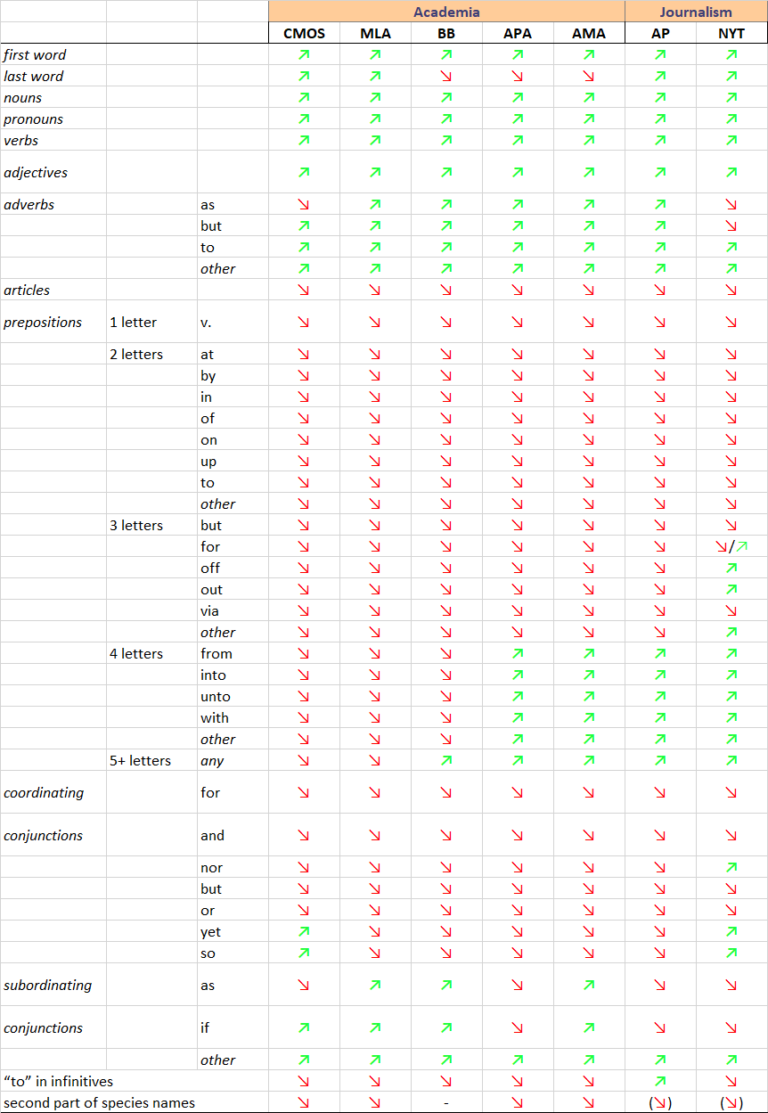
Below you find an image that shows when to capitalize a word for different academic and journalistic writing styles .
Examples
Green arrow (↑) indicates a major word, when a capital letter is used. Red arrow (↓) indicates a minor word, when only small letters are used.