Daily tech news
Daily tech news
- Scientists confirm one-dimensional electron behavior in phosphorus chainsFor the first time, researchers have shown that self-assembled phosphorus chains can host genuinely one-dimensional electron behavior. Using advanced imaging and spectroscopy techniques, they separated the signals from chains aligned in different directions to reveal their true nature. The findings suggest that squeezing the chains closer together could trigger a dramatic shift from semiconductor to […]
- A tiny light trap could unlock million qubit quantum computersA new light-based breakthrough could help quantum computers finally scale up. Stanford researchers created miniature optical cavities that efficiently collect light from individual atoms, allowing many qubits to be read at once. The team has already demonstrated working arrays with dozens and even hundreds of cavities. The approach could eventually support massive quantum networks with […]
- A strange in-between state of matter is finally observedWhen materials become just one atom thick, melting no longer follows the familiar rules. Instead of jumping straight from solid to liquid, an unusual in-between state emerges, where atomic positions loosen like a liquid but still keep some solid-like order. Scientists at the University of Vienna have now captured this elusive “hexatic” phase in real […]
- New catalyst makes plastic upcycling 10x more efficient than platinumScientists are finding new ways to replace expensive, scarce platinum catalysts with something far more abundant: tungsten carbide. By carefully controlling how tungsten carbide’s atoms are arranged at extremely high temperatures, researchers discovered a specific form that can rival platinum in key chemical reactions, including turning carbon dioxide into useful fuels and chemicals. Even more […]
- Engineers just created a “phonon laser” that could shrink your next smartphoneEngineers have created a device that generates incredibly tiny, earthquake-like vibrations on a microchip—and it could transform future electronics. Using a new kind of “phonon laser,” the team can produce ultra-fast surface waves that already play a hidden role in smartphones, GPS systems, and wireless tech. Unlike today’s bulky setups, this single-chip device could deliver […]
- An old jeweler’s trick could change nuclear timekeepingA team of physicists has discovered a surprisingly simple way to build nuclear clocks using tiny amounts of rare thorium. By electroplating thorium onto steel, they achieved the same results as years of work with delicate crystals — but far more efficiently. These clocks could be vastly more precise than current atomic clocks and work […]
Category
PIC16F877A Timer0 tutorial
The Timer0 module is an 8-bit timer/counter that is included with all 8-bit PIC MCU devices. The Timer0 is more than just a timer....
PIC Microcontrollers Timers
In this tutorial, we will learn what are "Timers"; we will explain this with examples using the Microcontroller PIC16F877A. For this tutorial is may be...
How to use interrupts in microcontrollers
In this tutorial we will learn how to use external interrupts in PIC microcontrollers. We will go in depth on how to set it up...
Interfacing 4×3 keypads with PIC16F877A
In this tutorial, we will provide an overview of the 4x3 membrane keypad. The keypad serves as a reliable and budget-friendly tool for having inputs...
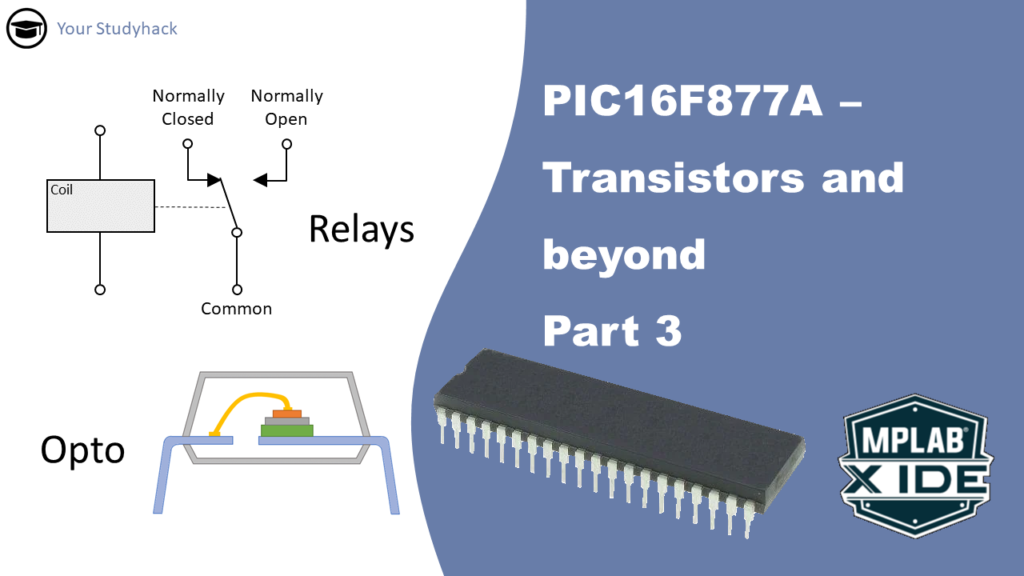
Control Possibilities with PIC16F877A: Relays, Optos, H Bridges (Part 3 of 3)
Most microcontrollers have limited current sink or current source on their pins, including the PIC16F877A. However, certain projects may require larger currents than the maximum...
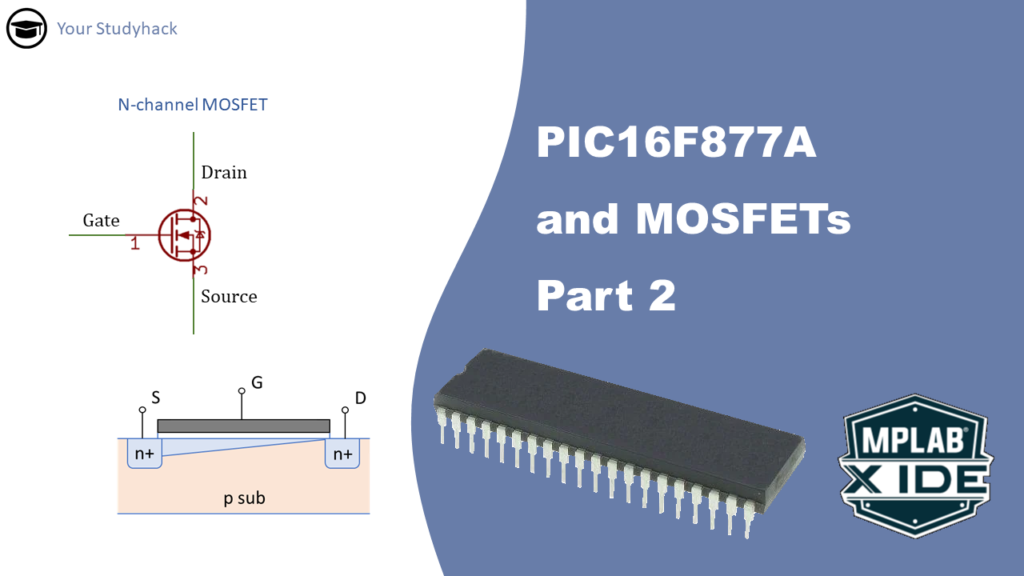
Interfacing PIC16F877A with MOSFETS (Part 2 of 3)
Most microcontrollers have a limited current sink or current source on the pins, the PIC16F877A is no exception. However, for certain projects you may want...