1. What is a literature review?
Literature reviews are typically the second chapter of a dissertation, following the Introduction. This guide will provide an overview of what literature reviews are and offer insights into the structure and format of literature reviews in the humanities, social sciences, and sciences.
A literature review is a written summary of key literature and sources on a specific topic or within a specific time period. It can include a simple overview of sources, but typically includes a more organized pattern and synthesis of the information. Synthesis in a literature review refers to the re-organization or reshuffling of information to provide a new interpretation of existing material or to combine it with new insights.
Why do we write a literature review?
Literature reviews serve as a guide to a particular topic, helping professionals stay current in their field and establishing credibility for scholars. They provide a comprehensive understanding of the literature and serve as a solid foundation for research.
To write the literature review, follow these 5 steps.
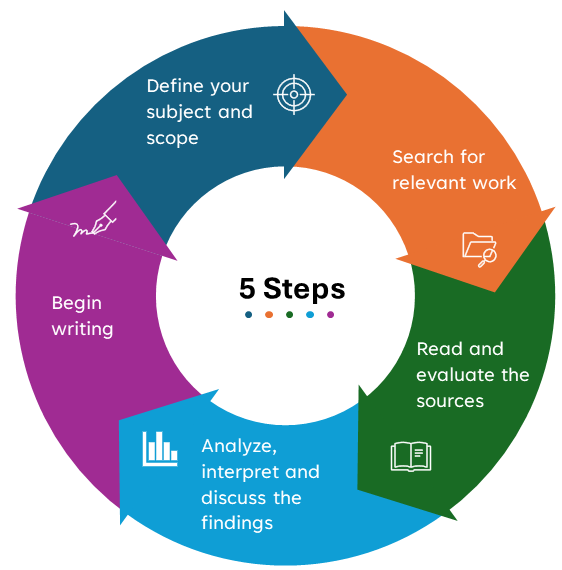
1.1 Define your subject and scope
When conducting a literature review, it is important to keep in mind that there are hundreds or even thousands of articles and books in all areas of study. The more narrowly you define your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read. This is important because your professor will likely not expect you to read everything on the topic, so narrowing your focus will make the process more manageable for you. Additionally, it is likely that your instructor is familiar with some published review articles in your field of study, which can serve as an excellent starting point for your literature review. These review articles summarize and critically evaluate the literature on a specific topic and can provide a comprehensive overview of the existing research in the field. Overall, it’s crucial to have a clear focus and defined scope for your literature review to make the process more efficient and manageable.
1.2 Search for relevant works
When conducting research, it is important to have a clear understanding of your topic and scope. Most likely, as you progressed in your research, you have already begun narrowing down your investigation to a specific topic. Having a clear understanding of your subject and scope will make it easier to define your research question and focus your literature review. One way to keep track of your topic and scope is by creating a list of keywords that are related to your research question. By including all of the key concepts and their synonyms, you will have a practical list of words to use when searching for relevant literature.
This list of keywords will help you to identify relevant sources and articles that are related to your research question. You can use these keywords to search online databases, library catalogs, and other resources. By having a clear and focused list of keywords, you will be able to quickly and easily identify the most relevant sources for your literature review. Additionally, by defining your research question, topic and scope, you can also set clear boundaries for your literature review and not get overwhelmed by too many sources that are not relevant to your research.
A list of useful databases and journals include:
- Your university’s library
- Google scholar
- Medline
- Inspec
- Econlit
1.3 Read and evaluate the sources
You probably won’t be able to read all the sources. In assessing each search, considerations should be given to:
- What is the author’s expertise in this particular field?
- Are the authors arguments supported by empirical evidence
- Does the selected source contribute to a more profound understanding of the subject?
When conducting a literature review, it is important to consider the specific requirements of your discipline. For certain fields, such as medicine, it is essential to have the most current information possible. In these cases, treatments for medical problems are constantly evolving and information that is even two years old could be obsolete. However, for other studies, a survey of the history of the literature may be more appropriate. This approach can provide valuable insights into how the perspective on a topic has changed over time.
For example, if you are writing a literature review for a medical study, it may be important to focus on the most recent research and treatment options. However, if you are writing a literature review for a study in the humanities or social sciences, a historical perspective may be more appropriate. In this case, you may need to look at literature that is several years or even decades old to understand how the field has developed over time.
It’s important to look at other current literature reviews in your field to get an idea of what is expected in your discipline. This will help you to understand the conventions and standards that are commonly used in your field and ensure that your literature review is in line with current expectations. Additionally, by looking at other literature reviews in your field you can also identify gaps in the literature and areas where more research is needed.
While reading, you should take notes that can later be used in the text. It is also very important to keep track of the sources you use with citations to avoid plagiarism. Keeping a list from the beginning will save time later in the process.
1.4 Analyze, interpret and discuss the findings
When reading the different sources, you should look for:
- Trends and patterns: Do approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Debates: Some papers have a section on debate, read it and get inspired.
- Conflicts and contradictions: Do different sources disagree? on what particular point and why?
- Gaps: Is there anything missing from literature? Is there anything that is based on weak data or requires more information to be made more clear?
1.5 Begin writing
A literature review is a critical evaluation of existing research on a specific topic. To organize your review effectively, it is important to include the following three elements:
Introduction: This section should provide an overview of the topic you are reviewing and its significance. You should also state the research question or objective of your review, as well as the scope and limitations of your study.
Body: This section is where you present and discuss the sources you have reviewed. The sources should be organized in a logical and consistent manner, such as chronologically, thematically, or methodologically. It is important to provide a clear summary of each source and to critically evaluate its strengths and weaknesses.
Conclusion/Recommendation: In this section, you should summarize your findings from the literature review and draw conclusions about the state of research on the topic. Additionally, you should provide recommendations for future research, such as areas that require further investigation or gaps in the existing literature that need to be addressed.
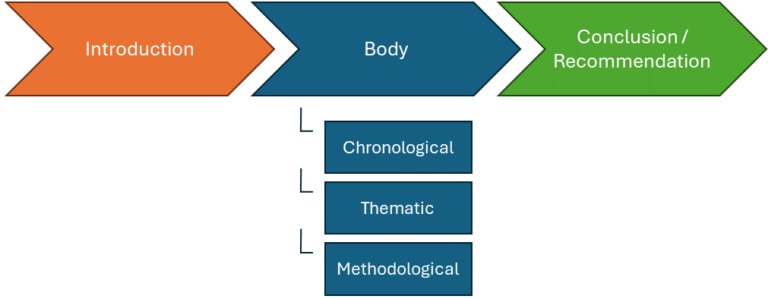
When organizing the sources in the body of your literature review, it is important to consider the most effective way to present the information. There are three main ways to organize sources: chronologically, thematically, or methodologically.
Chronological: Organizing sources by the date they were published can be useful for demonstrating the evolution of research on a particular topic. When using this approach, it is important to not only summarize the sources, but also look for patterns and key features that have shaped the field over time.
Thematic: This approach organizes sources around specific themes related to the topic of the review. While the progression of time may still be an important factor in a thematic review, the emphasis is on grouping sources by theme rather than by publication date.
Methodological: For some disciplines, different research methods are used to study a topic. Comparing the results and conclusions from different methods can be useful in understanding how the chosen research method has affected the outcome.
2. Key strategies to use for writing your literature.
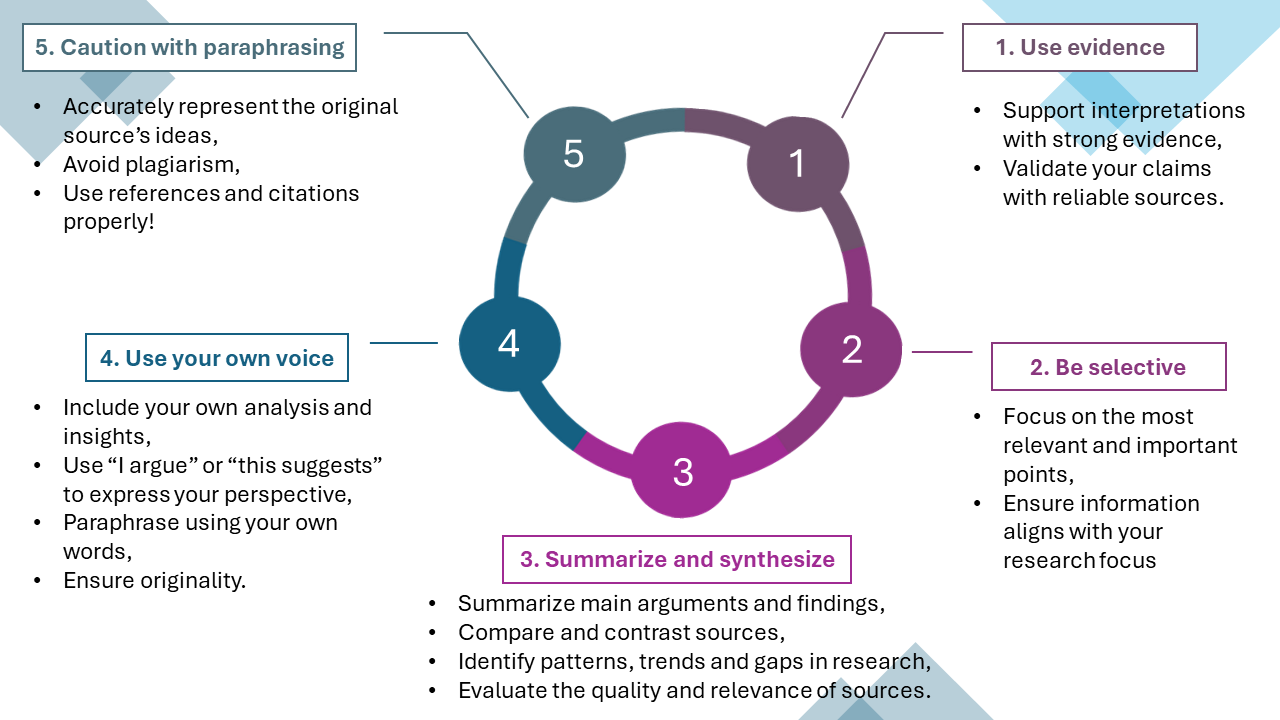
Caution with paraphrasing
When paraphrasing a source in a literature review, it is important to accurately represent the author’s information and use your own words. This is an important step to avoid plagiarism, which is the act of using someone else’s work without giving credit.
To paraphrase effectively, you should:
- Read the source carefully and make sure you understand the main ideas and arguments
- Take notes on the key points, using your own words
- Use your notes to write a new paragraph or section in your literature review, making sure to retain the meaning of the original source but using your own words.
It is also important to use references and citations when paraphrasing to give credit to the original author. Using an appropriate citation format and referencing the source in the text and in a bibliography, works cited or reference list will show that you have done the research and are aware of the existing literature.
Overall, paraphrasing is an important skill for a literature review as it allows you to accurately represent the ideas and arguments of others while avoiding plagiarism.
.
3. Example
In this literature review, we will focus on the topic of “graphene-based materials for energy storage.” Graphene is a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. It has attracted significant attention in recent years due to its unique electronic, mechanical, and thermal properties.
Research has shown that graphene-based materials have great potential for use in energy storage applications, such as supercapacitors and batteries. Studies have found that graphene can significantly improve the performance of these energy storage devices, by increasing their energy density and power density, and reducing their self-discharge rate.
Several studies have shown that graphene can be used to improve the performance of lithium-ion batteries. Researchers have found that incorporating graphene into the anode of a lithium-ion battery can significantly increase its capacity and improve its rate performance. Additionally, graphene has been found to be a promising material for use in supercapacitors due to its high surface area and excellent electrical conductivity.
However, despite the potential of graphene-based materials for energy storage, there are still several challenges that need to be addressed. Researchers have found that scaling up the production of graphene-based materials to industrial levels is still a major challenge. Additionally, the stability and durability of graphene-based materials in energy storage devices still need to be improved.
In conclusion, this literature review has shown that graphene-based materials have great potential for use in energy storage applications. However, more research is needed to address the challenges of scaling up production and improving the stability and durability of these materials. The dissertation aims to contribute to the existing knowledge by addressing these challenges and developing new methods of using Graphene-based materials for energy storage applications.
